
An agile approach to People Analytics projects
Originally published 29 March 2022
Technical projects are hard to deliver. The Agile Process is an iterative approach to delivery. It is widely used in software projects and can also be used to deliver People Analytics projects.
In this article, we discuss the problems that the Agile Process attempts to overcome. We also offer some tips for delivering successful projects.
The challenge of delivering complex projects
Delivering large or complex projects on time and within budget is always challenging. HR project teams can benefit from an Agile approach.
The Agile Process is an alternative to a Waterfall approach. Waterfall breaks the development process into a series of distinct phases. Each phase must complete before work begins on the next one. Waterfall is a popular approach with many advantages and works well when the requirements are well defined.
Agile is an attempt to manage projects with complex and changing requirements. It promotes rapid delivery and encourages early feedback.
Stakeholders have the flexibility to change the requirements during the project. Development teams no longer go dark for long periods or risk becoming isolated from the business objectives.
In some situations, a hybrid approach can be helpful. For example, a waterfall approach can define the high-level requirements, costs and timescales. Agile can then support an iterative or continuous delivery, working out the details of the requirements during the project (within the agreed scope).
How we help teams deliver agile analytics projects
Consultancy and advice
Strategic support to help teams set objectives, plan implementation and track delivery.
Implementation assistance
Jumpstart your analytics project with our data, reporting and implementation skills.
Team members and skills
A successful People Analytics project will often need many different skills. A typical project team might include people with the following skills or roles.
- Data architects, analysts and developers to implement the data migration and data engineering
- Presentation and visualisation to create the reports and dashboards
- Testing and quality assurance
- Infrastructure and deployment specialists
- Security and governance
Thinking in stories
In agile, user stories (or product backlog items) define the requirements. These are short descriptions of a desired feature or behaviour - written from the user's point of view.
Writing user stories encourages a focus on the business value to be delivered rather than the low-level technical details. User stories should be grouped into sets of features (or epics) to help with project planning.
Stories undergo refinement before they are ready to be implemented. This process should ensure that the requirements are clear enough to work from and that the user story describes the business value.
The following tasks are common to most People Analytics projects.
- Gather the user requirements
- Data capture, analysis and data science
- Build draft reports and visualisations
- Gather feedback from users
- Automate the data processing
- Testing and validation
- Deliver the working reports and visualisations
Deliver early and deliver often
The goal of Agile is to deliver working software early and often. Specific approaches to Agile vary, but in general terms, teams choose between a Kanban-style approach and a Scrum strategy.
Scrum - The Sprint-based Approach
Scrum teams often work in two-week delivery cycles, delivering software that works after every iteration. Shorter or longer delivery cycles are possible, but two-week cycles are a sweet spot for most teams.
The Product Owner and the team agree on the goals for each iteration. They decide which user stories to build and their priority. Prioritisation ensures the delivery of the most important stories when the sprint goals are too ambitious.
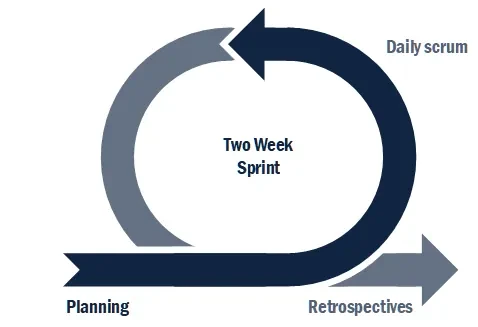
- The team agrees on the likely scale of effort needed to complete the user stories.
- The Product Owner defines the relative priority of the outstanding backlog.
- The Product Owner can continuously refine the project while allowing the team to commit to what will be delivered.
Breaking the work into separate chunks encourages stakeholders to give early and regular feedback. Adopting an agile approach allows your People Analytics team to deliver reports and dashboards regularly and often. This approach provides users with tangible output to review and comment on.
Kanban - The Continuous Delivery Approach
Kanban has its origins in Japanese manufacturing. The Kanban approach removes the ceremonies associated with Scrum (such as sprint planning and retrospective reviews). In their place is a continuous review of the tasks and their priorities. As a concept, each task flows through a series of stages such as "to do", "in progress", "in QA", and "done".
The continuous flow of Kanban is a more flexible approach and lends itself well to creating a product roadmap.
The more flexible structure doesn't have to mean a lack of management or oversight. For example, the lead time from a feature appearing on the wish list to its completion is helpful. A similar cycle time metric shows the average time from starting a piece of work to its completion. Long lead times might indicate a need for more resources. Long cycle times might suggest that more simple user stories would reduce risk. Long cycle times sometimes indicate a lack of clarity in the user stories.
Choosing between Kanban and Scrum
Many teams have had great success with both Kanban and Scrum styles of Agile delivery. The choice will depend on how complex the project is, how often requirements are likely to change, the availability of the stakeholders, the skills of the team, the availability of the resources and more factors.
Some teams find two-week delivery unachievable for a variety of reasons. Scrum can lead to a perception that these teams cannot deliver and are failing. Kanban can highlight the ability of these teams and that they are regularly delivering business value.
Advantages and disadvantages of Kanban
- Regular opportunities to celebrate and highlight success.
- Comparing priorities of stories can be easier.
- Can set teams up for regular failure.
- Needs a strong Product Owner to work closely with the team.
Advantages and disadvantages of Scrum
- Minimises regular meetings and emphasises delivery.
- Teams are continuously delivering without unnecessary delay.
- Stakeholders can change their minds rather than wait for the next iteration.
- Lends itself to a trouble ticket style of working.
- Perceived lack of management information and organisation control.
On reflection...
Early feedback is crucial to a successful agile project. Short delivery cycles encourage smaller chunks of work and allow users to offer comments. Teams often find it helpful to review what they have achieved (and what they can improve) in regular retrospective sessions.
People Analytics projects, by their nature, often involve people with diverse backgrounds and skill sets. Projects typically need people to collect and process the source data, others to analyse the data, and a different group to work on presenting the reports.
Regular communication and reviews can help manage the risks of people working alone. Attention focuses on how to deliver to stakeholders and how to meet the requirements of the end-users.
Next steps
We help organisations of all sizes plan and implement people analytics.
Please get in touch if you would like to discuss how we can help you.

Like this article?
Please share and follow us...
To find out more, please contact us...
Services
Our skills
Viewpoint BI is powered by HR-Fundamentals ltd. © HR-Fundamentals ltd.
Registered in England and Wales, number 0461 5583.
20 Market Place, Kingston upon Thames KT1 1JP